CONTENTS
- DESCRIPTION
- SYNOPSIS
- EXAMPLES
- WORKBOOK METHOD
- WORKSHEET METHOD
- PAGE SET-UP METHOD
- CELL FORMATTING
- FORMAT METHODS
- COLORS IN EXCEL
- DATES AND TIME IN EXCEL
- OUTLINES AND GROUPING IN EXCEL
- DATA VALIDATION IN EXCEL
- CONDITIONAL FORMATTING IN EXCEL
- SPARKLINES IN EXCEL
- TABLES IN EXCEL
- FORMURAS AND FUNCTIONS IN EXCEL
- CHART METHODS
- CHART FONTS
- CHART LAYOUT
- SHAPE
- COMPATIBILITY WITH WRITEEXCEL
CONDITIONAL FORMATTING IN EXCEL
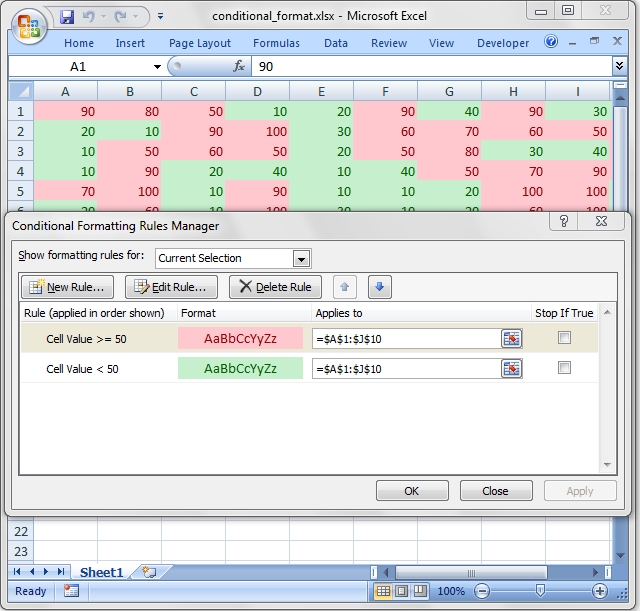
Conditional formatting is a feature of Excel which allows you to apply a format to a cell or a range of cells based on a certain criteria.
For example the following criteria is used to highlight cells >= 50 in red in the
conditional_format.rb
example from the distro:
# Write a conditional format over a range.
worksheet.conditional_formatting('B3:K12',
{
type: 'cell',
criteria: '>=',
value: 50,
format: format1
}
)
conditional_formatting(row, col, { parameter: ‘value’, … } )
The conditional_formatting() method is used to apply formatting based on user
defined criteria to an WriteXLSX file.
It can be applied to a single cell or a range of cells. You can pass 3 parameters such as (row, col, {…}) or 5 parameters such as (first_row, first_col, last_row, last_col, {…}). You can also use A1 style notation. For example:
worksheet.conditional_formatting(0, 0, {...})
worksheet.conditional_formatting(0, 0, 4, 1, {...})
# Which are the same as:
worksheet.conditional_formatting('A1', {...})
worksheet.conditional_formatting('A1:B5', {...})
See also the note about “Cell notation” for more information.
Using A1 style notation is also possible to specify non-contiguous ranges, separated by a comma. For example:
worksheet.conditional_formatting('A1:D5,A8:D12', {...})
The last parameter in conditional_formatting() must be a hash containing
the parameters that describe the type and style of the data validation.
The main parameters are:
:type
:format
:criteria
:value
:minimum
:maximum
Other, less commonly used parameters are:
:min_type
:mid_type
:max_type
:min_value
:mid_value
:max_value
:min_color
:mid_color
:max_color
:bar_color
:bar_only
:bar_solid
:bar_negative_color
:bar_negative_border_color
:bar_negative_color_same
:bar_negative_border_color_same
:bar_no_border
:bar_direction
:bar_axis_position
:bar_axis_color
:data_bar_2010
:icon_style
:icons
:reverse_icons
:icons_only
:stop_if_true
:multi_range
Additional parameters which are used for specific conditional format types are shown in the relevant sections below.
:type
This parameter is passed in a hash to conditional_formatting().
The :type parameter is used to set the type of conditional formatting that
you wish to apply. It is always required and it has no default value.
Allowable type values and their associated parameters are:
Type Parameters
==== ==========
cell criteria
value
minimum
maximum
format
date criteria
value
minimum
maximum
format
time_period criteria
format
text criteria
value
format
average criteria
format
duplicate format
unique format
top criteria
value
format
bottom criteria
value
format
blanks format
no_blanks format
errors format
no_errors format
formula criteria
format
2_color_scale min_type
max_type
min_value
max_value
min_color
max_color
3_color_scale min_type
mid_type
max_type
min_value
mid_value
max_value
min_color
mid_color
max_color
data_bar min_type
max_type
min_value
max_value
bar_only
bar_color
bar_solid*
bar_negative_color*
bar_negative_border_color*
bar_negative_color_same*
bar_negative_border_color_same*
bar_no_border*
bar_direction*
bar_axis_position*
bar_axis_color*
data_bar_2010*
icon_set icon_style
reverse_icons
icons
icons_only
Data bar parameters marked wth (*) are only available in Excel 2010 and later. Files that use these properties can still be opened in Excel 2007 but the data bars will be displayed without them.
type: ‘cell’
This is the most common conditional formatting type. It is used when a format is applied to a cell based on a simple criterion. For example:
worksheet.conditional_formatting('A1',
{
type: 'cell',
criteria: 'greater than',
value: 5,
format: red_format,
}
)
Or, using the between criteria:
worksheet.conditional_formatting('C1:C4',
{
type: 'cell',
criteria: 'between',
minimum: 20,
maximum: 30,
format: green_format,
}
)
:criteria
The criteria parameter is used to set the criteria by which the cell data
will be evaluated. It has no default value. The most common criteria as
applied to { type: 'cell' } are:
'between'
'not between'
'equal to' | '==' | '='
'not equal to' | '!=' | '<>'
'greater than' | '>'
'less than' | '<'
'greater than or equal to' | '>='
'less than or equal to' | '<='
You can either use Excel’s textual description strings, in the first column above, or the more common symbolic alternatives.
Additional criteria which are specific to other conditional format types are shown in the relevant sections below.
:value
The value is generally used along with the criteria parameter to set the rule by which the cell data will be evaluated.
type: 'cell',
criteria: '>',
value: 5
format: format,
The value property can also be an cell reference.
type: 'cell',
criteria: '>',
value: '$C$1',
format: format,
:format
The format parameter is used to specify the format that will be applied to
the cell when the conditional formatting criterion is met.
The format is created using the add_format() method in the same way as cell
formats:
format = workbook.add_format(bold: 1, italic: 1)
worksheet.conditional_formatting('A1',
{
type: 'cell',
criteria: '>',
value: 5
format: format,
}
)
The conditional format follows the same rules as in Excel: it is superimposed over the existing cell format and not all font and border properties can be modified. Font properties that can’t be modified are font name, font size, superscript and subscript. The border property that cannot be modified is diagonal borders.
Excel specifies some default formats to be used with conditional formatting. You can replicate them using the following WriteXLSX formats:
# Light red fill with dark red text.
format1 = workbook.add_format(
bg_color: '#FFC7CE',
color: '#9C0006',
)
# Light yellow fill with dark yellow text.
format2 = workbook.add_format(
bg_color: '#FFEB9C',
color: '#9C6500',
)
# Green fill with dark green text.
format3 = workbook.add_format(
bg_color: '#C6EFCE',
color: '#006100',
)
:minimum
The minimum parameter is used to set the lower limiting value when the
criteria is either ‘between’ or ‘not between’:
validate: 'integer',
criteria: 'between',
minimum: 1,
maximum: 100,
:maximum
The maximum parameter is used to set the upper limiting value when the
criteria is either ‘between’ or ‘not between’. See the previous example.
type: ‘date’
The date type is the same as the cell type and uses the same criteria
and values. However it allows the :value, :minimum and :maximum properties to be
specified in the ISO8601
yyyy-mm-ddThh:mm:ss.sss date format which is detailed in the
write_date_time() method.
worksheet.conditional_formatting('A1:A4',
{
type: 'date',
criteria: 'greater than',
value: '2011-01-01T',
format: format,
}
)
type: ‘time_period’
The time_period type is used to specify Excel’s “Dates Occurring” style
conditional format.
worksheet.conditional_formatting('A1:A4',
{
type: 'time_period',
criteria: 'yesterday',
format: format,
}
)
The period is set in the :criteria and can have one of the following values:
criteria: 'yesterday',
criteria: 'today',
criteria: 'last 7 days',
criteria: 'last week',
criteria: 'this week',
criteria: 'next week',
criteria: 'last month',
criteria: 'this month',
criteria: 'next month'
type: ‘text’
The text type is used to specify Excel’s “Specific Text” style conditional
format. It is used to do simple string matching using the :criteria and
:value parameters:
worksheet.conditional_formatting('A1:A4',
{
type: 'text',
criteria: 'containing',
value: 'foo',
format: format,
}
)
The :criteria can have one of the following values:
criteria: 'containing',
criteria: 'not containing',
criteria: 'begins with',
criteria: 'ends with',
The :value parameter should be a string or single character.
type: ‘average’
The average type is used to specify Excel’s “Average” style conditional format.
worksheet.conditional_formatting('A1:A4',
{
type: 'average',
criteria: 'above',
format: format,
}
)
The type of average for the conditional format range is specified by the :criteria:
criteria: 'above',
criteria: 'below',
criteria: 'equal or above',
criteria: 'equal or below',
criteria: '1 std dev above',
criteria: '1 std dev below',
criteria: '2 std dev above',
criteria: '2 std dev below',
criteria: '3 std dev above',
criteria: '3 std dev below',
type: ‘duplicate’
The duplicate type is used to highlight duplicate cells in a range:
worksheet.conditional_formatting('A1:A4',
{
type: 'duplicate',
format: format,
}
)
type: ‘unique’
The unique type is used to highlight unique cells in a range:
worksheet.conditional_formatting('A1:A4',
{
type: 'unique',
format: format,
}
)
type: ‘top’
The top type is used to specify the top n values by number or percentage
in a range:
worksheet.conditional_formatting('A1:A4',
{
type: 'top',
value: 10,
format: format,
}
)
The :criteria can be used to indicate that a percentage condition is required:
worksheet.conditional_formatting('A1:A4',
{
type: 'top',
value: 10,
criteria: '%',
format: format,
}
)
type: ‘bottom’
The bottom type is used to specify the bottom n values by number or percentage
in a range.
It takes the same parameters as top, see above.
type: ‘blanks’
The blanks type is used to highlight blank cells in a range:
worksheet.conditional_formatting('A1:A4',
{
type: 'blanks',
format: format,
}
)
type: ‘no_blanks’
The no_blanks type is used to highlight non blank cells in a range:
worksheet.conditional_formatting('A1:A4',
{
type: 'no_blanks',
format: format,
}
)
type: ‘errors’
The errors type is used to highlight error cells in a range:
worksheet.conditional_formatting('A1:A4',
{
type: 'errors',
format: format,
}
)
type: ‘no_errors’
The no_errors type is used to highlight non error cells in a range:
worksheet.conditional_formatting('A1:A4',
{
type: 'no_errors',
format: format,
}
)
type: ‘formula’
The formula type is used to specify a conditional format based on a user
defined formula:
worksheet.conditional_formatting('A1:A4',
{
type: 'formula',
criteria: '=$A$1 > 5',
format: format,
}
)
The formula is specified in the criteria.
type: ‘2_color_scale’
The 2_color_scale type is used to specify Excel’s “2 Color Scale”
style conditional format.
worksheet.conditional_formatting('A1:A12',
{
type: '2_color_scale',
}
)
This conditional type can be modified with :min_type, :max_type,
:min_value, :max_value, :min_color and :max_color, see below.
type: ‘3_color_scale’
The 3_color_scale type is used to specify Excel’s “3 Color Scale”
style conditional format.
worksheet.conditional_formatting('A1:A12',
{
type: '3_color_scale',
}
)
This conditional type can be modified with :min_type, :mid_type,
:max_type, :min_value, :mid_value, :max_value, :min_color,
:mid_color and :max_color, see below.
type: ‘data_bar’
The data_bar type is used to specify Excel’s “Data Bar” style conditional format.
worksheet.conditional_formatting('A1:A12',
{
type: 'data_bar',
}
)
This data bar conditional type can be modified with the following parameters, which are explained in the sections below. These properties were available in the original xlsx file specification used in Excel 2007:
:min_type
:max_type
:min_value
:max_value
:bar_color
:bar_only
In Excel 2010 additional data bar properties were added such as solid (non-gradient) bars and control over how negative values are displayed. These properties can be set using the following parameters:
:bar_solid
:bar_negative_color
:bar_border_color
:bar_negative_border_color
:bar_negative_color_same
:bar_negative_border_color_same
:bar_no_border
:bar_direction
:bar_axis_position
:bar_axis_color
:data_bar_2010
Files that use these Excel 2010 properties can still be opened in Excel 2007 but the data bars will be displayed without them.
:min_type, :mid_type, :max_type
The :min_type and :max_type properties are available when the conditional
formatting type is 2_color_scale, 3_color_scale or data_bar.
The :mid_type is available for 3_color_scale.
The properties are used as follows:
worksheet.conditional_formatting('A1:A12',
{
type: '2_color_scale',
min_type: 'percent',
max_type: 'percent',
}
)
The available min/mid/max types are:
min (for min_type only)
num
percent
percentile
formula
max (for max_type only)
:min_value, :mid_value, :max_value
The :min_value and :max_value properties are available when the conditional
formatting type is 2_color_scale, 3_color_scale or data_bar.
The :mid_value is available for 3_color_scale.
The properties are used as follows:
worksheet.conditional_formatting('A1:A12',
{
type: '2_color_scale',
min_value: 10,
max_value: 90,
}
)
:min_color, :mid_color, :max_color, :bar_color
The :min_color and :max_color properties are available when the conditional
formatting type is 2_color_scale, 3_color_scale or data_bar.
The :mid_color is available for 3_color_scale.
The properties are used as follows:
worksheet.conditional_formatting('A1:A12',
{
type: '2_color_scale',
min_color: "#C5D9F1",
max_color: "#538ED5",
}
)
The color can be specifies as an WriteXLSX color index or, more usefully, as a HTML style RGB hex number, as shown above.
:bar_only
The bar_only parameter property displays a bar data but not the data in the cells:
worksheet.conditional_formatting(
'D3:D14',
{
type: 'data_bar',
bar_only: 1
}
)
:bar_solid
The C
worksheet.conditional_formatting(
'H3:H14',
{
type: 'data_bar',
bar_solid: 1
}
)
Note, this property is only visible in Excel 2010 and later.
:bar_negative_color
The bar_negative_color parameter is used to set the color fill for the negative portion of a data bar.
The color can be specified as an WriteXLSX color index or as a HTML style RGB hex number, as shown in the other examples.
Note, this property is only visible in Excel 2010 and later.
:bar_border_color
The bar_border_color parameter is used to set the border color of a data bar.
The color can be specified as an WriteXLSX color index or as a HTML style RGB hex number, as shown in the other examples.
Note, this property is only visible in Excel 2010 and later.
:bar_negative_border_color
The bar_negative_border_color parameter is used to set the border color of the negative portion of a data bar.
The color can be specified as an WriteXLSX color index or as a HTML style RGB hex number, as shown in the other examples.
Note, this property is only visible in Excel 2010 and later.
:bar_negative_color_same
The C
worksheet.conditional_formatting(
'N3:N14',
{
type: 'data_bar',
bar_negative_color_same: 1,
bar_negative_border_color_same: 1
}
)
Note, this property is only visible in Excel 2010 and later.
:bar_negative_border_color_same
The bar_negative_border_color_same parameter sets the border color for the negative portion of a data bar to be the same as the border color for the positive portion of the data bar.
Note, this property is only visible in Excel 2010 and later.
:bar_no_border
The bar_no_border parameter turns off the border of a data bar.
Note, this property is only visible in Excel 2010 and later, however the default in Excel 2007 is not to have a border.
:bar_direction
The bar_direction parameter sets the direction for data bars. This property can be either left for left-to-right or right for right-to-left. If the property isn’t set then Excel will adjust the position automatically based on the context:
worksheet.conditional_formatting(
'J3:J14',
{
type: 'data_bar',
bar_direction: 'right'
}
)
Note, this property is only visible in Excel 2010 and later.
:bar_axis_position
The bar_axis_position parameter sets the position within the cells for the axis that is shown in data bars when there are negative values to display. The property can be either middle or none. If the property isn’t set then Excel will position the axis based on the range of positive and negative values.
Note, this property is only visible in Excel 2010 and later.
:bar_axis_color
The bar_axis_color parameter sets the color for the axis that is shown in data bars when there are negative values to display.
The color can be specified as an WriteXLSX color index or as a HTML style RGB hex number, as shown in the other examples.
Note, this property is only visible in Excel 2010 and later.
:data_bar_2010
The C
worksheet->conditional_formatting(
'L3:L14',
{
type: 'data_bar',
data_bar_2010: 1
}
)
Note, this property is only visible in Excel 2010 and later.
:stop_if_true
The :stop_if_true parameter, if set to a true value, will enable the “stop if true” feature on the conditional formatting rule, so that subsequent rules are not examined for any cell on which the conditions for this rule are met.
:icon_set
The icon_set type is used to specify a conditional format with a set of icons such as traffic lights or arrows:
worksheet.conditional_formatting( 'A1:C1',
{
type: 'icon_set',
icon_style: '3_traffic_lights'
}
)
The icon set style is specified by the icon_style parameter. Valid options are:
3_arrows
3_arrows_gray
3_flags
3_signs
3_symbols
3_symbols_circled
3_traffic_lights
3_traffic_lights_rimmed
4_arrows
4_arrows_gray
4_ratings
4_red_to_black
4_traffic_lights
5_arrows
5_arrows_gray
5_quarters
5_ratings
The criteria, type and value of each icon can be specified using the icon array of hash refs with optional criteria, type and value parameters:
worksheet.conditional_formatting( 'A1:D1',
{
type: 'icon_set',
icon_style: '4_red_to_black',
icons: [ {criteria: '>', type: 'number', value: 90},
{criteria: '>=', type: 'percentile', value: 50},
{criteria: '>', type: 'percent', value: 25}
]
}
)
The icons criteria parameter should be either < >= > or < > >. The default criteria is < >= >.
The icons type parameter should be one of the following values:
number
percentile
percent
formula
The default type is percent.
The icons value parameter can be a value or formula:
worksheet.conditional_formatting( 'A1:D1',
{
type: 'icon_set',
icon_style: '4_red_to_black',
icons: [ {value: 90},
{value: 50},
{value: 25}
]
}
)
Note: The icons parameters should start with the highest value and with each subsequent one being lower. The default value is (n * 100) / number_of_icons. The lowest number icon in an icon set has properties defined by Excel. Therefore in a n icon set, there is no n-1 hash of parameters.
The order of the icons can be reversed using the reverse_icons parameter:
worksheet.conditional_formatting( 'A1:C1',
{
type: 'icon_set',
icon_style: '3_arrows',
reverse_icons: 1
}
)
The icons can be displayed without the cell value using the icons_only parameter:
worksheet.conditional_formatting( 'A1:C1',
{
type: 'icon_set',
icon_style: '3_flags',
icons_only: 1
}
)
Conditional Formatting Examples
Example 1. Highlight cells greater than an integer value.
worksheet.conditional_formatting('A1:F10',
{
type: 'cell',
criteria: 'greater than',
value: 5,
format: format
}
)
Example 2. Highlight cells greater than a value in a reference cell.
worksheet.conditional_formatting('A1:F10',
{
type: 'cell',
criteria: 'greater than',
value: '$H$1',
format: format
}
)
Example 3. Highlight cells greater than a certain date:
worksheet.conditional_formatting('A1:F10',
{
type: 'date',
criteria: 'greater than',
value: '2011-01-01T',
format: format
}
)
Example 4. Highlight cells with a date in the last seven days:
worksheet.conditional_formatting('A1:F10',
{
type: 'time_period',
criteria: 'last 7 days',
format: format
}
)
Example 5. Highlight cells with strings starting with the letter b:
worksheet.conditional_formatting('A1:F10',
{
type: 'text',
criteria: 'begins with',
value: 'b',
format: format
}
)
Example 6. Highlight cells that are 1 std deviation above the average for the range:
worksheet.conditional_formatting('A1:F10',
{
type: 'average',
format: format
}
)
Example 7. Highlight duplicate cells in a range:
worksheet.conditional_formatting('A1:F10',
{
type: 'duplicate',
format: format
}
)
Example 8. Highlight unique cells in a range.
worksheet.conditional_formatting('A1:F10',
{
type: 'unique',
format: format
}
)
Example 9. Highlight the top 10 cells.
worksheet.conditional_formatting('A1:F10',
{
type: 'top',
value: 10,
format: format
}
)
Example 10. Highlight blank cells.
worksheet.conditional_formatting('A1:F10',
{
type: 'blanks',
format: format
}
)
Example 11. Set traffic light icons in 3 cells:
worksheet.conditional_formatting( 'A1:C1',
{
type: 'icon_set',
icon_style: '3_traffic_lights'
}
)
See also the
conditional_format.rb
example program in EXAMPLES.