CONTENTS
- DESCRIPTION
- SYNOPSIS
- EXAMPLES
- WORKBOOK METHOD
- WORKSHEET METHOD
- PAGE SET-UP METHOD
- CELL FORMATTING
- FORMAT METHODS
- COLORS IN EXCEL
- DATES AND TIME IN EXCEL
- OUTLINES AND GROUPING IN EXCEL
- DATA VALIDATION IN EXCEL
- CONDITIONAL FORMATTING IN EXCEL
- SPARKLINES IN EXCEL
- TABLES IN EXCEL
- FORMURAS AND FUNCTIONS IN EXCEL
- CHART METHODS
- CHART FONTS
- CHART LAYOUT
- SHAPE
- COMPATIBILITY WITH WRITEEXCEL
SYNOPSIS
To create a simple Excel file with a Stock chart using WriteXLSX:
require 'write_xlsx'
workbook = WriteXLSX.new('chart.xlsx')
worksheet = workbook.add_worksheet
chart = workbook.add_chart(type: 'stock')
# Add a series for each High-Low-Close.
chart.add_series(
categories: '=Sheet1!$A$2:$A$6',
values: '=Sheet1!$B$2:$B$6'
)
chart.add_series(
categories: '=Sheet1!$A$2:$A$6',
values: '=Sheet1!$C$2:$C$6'
)
chart.add_series(
categories: '=Sheet1!$A$2:$A$6',
values: '=Sheet1!$D$2:$D$6'
)
# Add the worksheet data the chart refers to.
# ... See the full example below.
.........
workbook.close
DESCRIPTION
This module implements Stock charts for WriteXLSX.
The chart object is created via the Workbook add_chart() method:
chart = workbook.add_chart(type: 'stock')
Once the object is created it can be configured via the following methods that are common to all chart classes:
chart.add_series
chart.set_x_axis
chart.set_y_axis
chart.set_title
These methods are explained in detail in Chart. Class specific methods or settings, if any, are explained below.
Column Chart Methods
There aren’t currently any stock chart specific methods.
The default Stock chart is a High-Low-Close chart. A series must be added for each of these data sources.
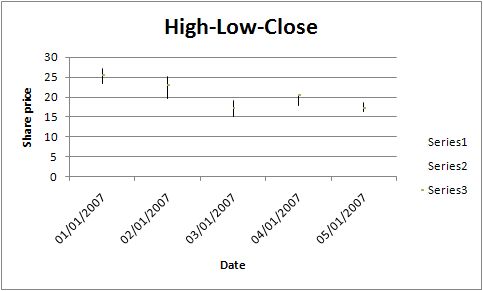
EXAMPLE
Here is a comlete example that demonstrates most of the available feature when creating a chart.
require 'write_xlsx'
workbook = WriteXLSX.new('chart_stock.xlsx')
worksheet = workbook.add_worksheet
bold = workbook.add_format(bold: 1)
date_format = workbook.add_format(num_format: 'dd/mm/yyyy')
chart = workbook.add_chart(type: 'stock', embedded: 1)
# Add the worksheet data that the charts will refer to.
headings = [ 'Date', 'High', 'Low', 'Close' ]
data = [
[ '2007-01-01T', '2007-01-02T', '2007-01-03T', '2007-01-04T', '2007-01-05T' ],
[ 27.2, 25.03, 19.05, 20.34, 18.5 ],
[ 23.49, 19.55, 15.12, 17.84, 16.34 ],
[ 25.45, 23.05, 17.32, 20.45, 17.34 ]
]
worksheet.write('A1', headings, bold)
(0..4).each do |row|
worksheet.write_date_time(row+1, 0, data[0][row], date_format )
worksheet.write( row+1, 1, data[1][row] )
worksheet.write( row+1, 2, data[2][row] )
worksheet.write( row+1, 3, data[3][row] )
end
worksheet.set_column('A:D', 11)
# Add a series for each of the High-Low-Close columns.
chart.add_series(
categories: '=Sheet1!$A$2:$A$6',
values: '=Sheet1!$B$2:$B$6'
)
chart.add_series(
categories: '=Sheet1!$A$2:$A$6',
values: '=Sheet1!$C$2:$C$6'
)
chart.add_series(
categories: '=Sheet1!$A$2:$A$6',
values: '=Sheet1!$D$2:$D$6'
)
# Add a chart title and some axis labels.
chart.set_title (name: 'High-Low-Close')
chart.set_x_axis(name: 'Date')
chart.set_y_axis(name: 'Share price')
worksheet.insert_chart('E9', chart)
workbook.close
This will produce a chart that looks like this: